Alignments¶
AtomGroup instances can store multiple coordinate sets,
i.e. multiple models from an NMR structure. This example shows how to align
such coordinate sets using alignCoordsets() function.
Resulting AtomGroup will have its coordinate sets superposed onto
the active coordinate set selected by the user.
Parse an NMR structure¶
We start by importing everything from the ProDy package:
In [1]: from prody import *
In [2]: from pylab import *
In [3]: ion()
We use 1joy that contains 21 models homodimeric domain of EnvZ protein from E. coli.
In [4]: pdb = parsePDB('1joy')
In [5]: pdb.numCoordsets()
Out[5]: 21
Calculate RMSD¶
In [6]: rmsds = calcRMSD(pdb)
In [7]: rmsds.mean()
Out[7]: 37.506911678400954
This function calculates RMSDs with respect to the active coordinate set, which is the first model in this case.
In [8]: showProtein(pdb);
In [9]: pdb.setACSIndex(1) # model 2 in PDB is now the active coordinate set
In [10]: showProtein(pdb);
In [11]: legend();
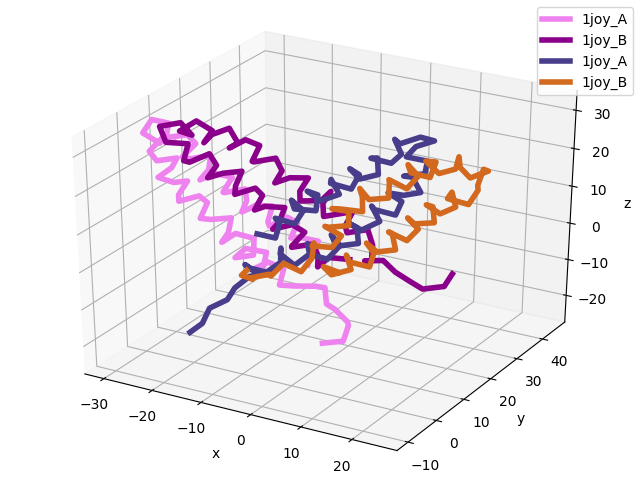
Align coordinate sets¶
We will superpose all models onto the first model in the file using based on Cα atom positions:
In [12]: pdb.setACSIndex(0)
In [13]: alignCoordsets(pdb.calpha);
To use all backbone atoms, pdb.backbone can be passed as argument. See
Atom Selections for more information on making selections.
Coordinate sets are superposed onto the first model (the active coordinate set).
In [14]: rmsds = calcRMSD(pdb)
In [15]: rmsds.mean()
Out[15]: 3.276891215176855
In [16]: showProtein(pdb);
In [17]: pdb.setACSIndex(1) # model 2 in PDB is now the active coordinate set
In [18]: showProtein(pdb);
In [19]: legend();
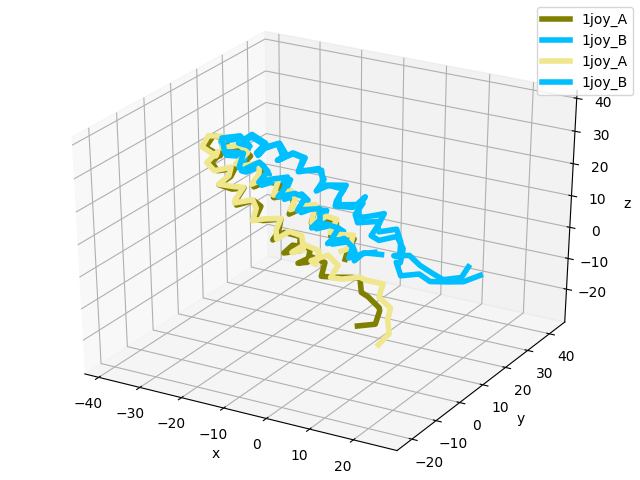
Write aligned coordinates¶
Using writePDB() function, we can write the aligned
coordinate sets in PDB format:
In [20]: writePDB('1joy_aligned.pdb', pdb)
Out[20]: '1joy_aligned.pdb'
